20.01. Ponavljanje gradiva (1.čas): HTML DOM
1. Šta je DOM?
DOM (Document Object Model) je hijerarhijska struktura web stranice.
U DOM-u se definišu:
- HTML elementi kao objekti (engl. objects)
- Svojstva svih HTML elemenata (engl. properties)
- Metode za pristup svim HTML elementima (engl. methods)
- Događaji za sve HTML elemente (engl. events)
Kada se stranica učita, web browser kreira DOM kao stablo objekata gde su HTML tagovi čvorovi tog stabla. DOM nam omogućava da preuzmemo, izmenimo, dodamo ili izbrišemo HTML elemente (npr pomoću JavaScript-a ili nekog drugog jezika).
Glavne funkcionalnosti DOM-a:
- Pristup HTML elementima kao objektima.
- Manipulacija svojstvima i metodama elemenata.
- Reagovanje na događaje.
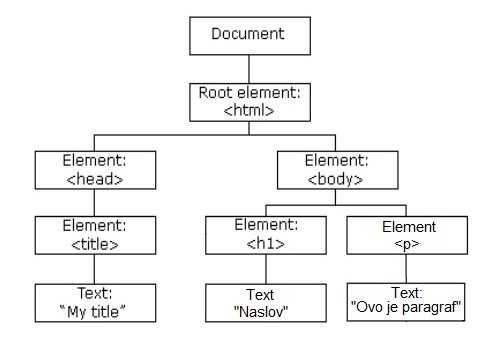
| <html> <head> <title> My title </title> </head> <body> <h1>Naslov</h1> <p>Ovo je paragraf.</p> </body> </html> |
 |
|---|
Svaki čvor (engl. node) može da ima roditelja (parent), dete (child) ili brata/sestru (sibling). Analogija može da se postavi u odnosu na porodično stablo (roditelji, deca, braća i sestre).
U ovom primeru:
<body>i<head>su deca elementa<html>.<h1>i<p>su deca elementa<body>.- rečju
siblingnazivamo odnos između<h1>i<p>
U ovaj primer treba dodati 2 reda:
<p> drugi red teksta </p>
U cilju ilustracije kretanja kroz stablo DOM-a, u konzoli ćemo upotrebiti nekoliko praktičnih primera navigacije kroz DOM:
-
Pristup roditeljskom elementu:
const parent = document.getElementById("demo").parentNode;console.log(parent); -
Pristup detetu elementa:
const child = document.getElementById("demo").firstChild;console.log(child); -
Pristup sledećem/bratskom elementu:
const sibling = document.getElementById("demo").nextElementSibling;console.log(sibling);
3. Pristup HTML elementima
-
Pristup elementima se vrši pomoću JavaScript metoda:
document.getElementById("id");document.getElementsByClassName("class");document.getElementsByTagName("tag");document.querySelector("selector");document.querySelectorAll("selector");
Primer 1: Dodati paragraf id="proba" kojem će da se promeni sadržaj:
-
Promena sadržaja:
<p id="proba">Ovo je originalni tekst.</p>
<script>
document.getElementById("proba").innerHTML = "Promenjeni tekst!";
</script>
Primer 2: Dodati dugme ispod. Klikom na dugme treba da se promeni boja teksta paragrafa sa id="proba":
-
Promena stila:
<button onclick="promeniBoju()">Promeni boju</button>
<script>
function promeniBoju() {
document.getElementById("proba").style.color = "blue";
}
</script>
Primer 3: dodati još jedan paragraf, tako što se pomoću JavaScripta kreira i dodaje novi element na stranicu.
-
Dodavanje elemenata:
let noviElement = document.createElement("p");noviElement.textContent = "Ovo je novi paragraf.";document.body.appendChild(noviElement);
Primer 4: Izvršiti promenu stila tako da je boja slova crvena ako je miš iznad njih, a crna onda kad miš izađe iz oblasti paragrafa koji ima id="demo"
-
Primer promena stila na
mouseoverdogađaju:const demo = document.getElementById("demo");demo.onmouseover = function () {demo.style.color = "red";};demo.onmouseout = function () {demo.style.color = "black";};
Primer 5: Dodati jedno input polje i postaviti mu id="input". Kako korisnik kuca, tako treba u konzoli ispisivati sadržaj input polja (value).
-
Reakcija na unos u polje teksta:
const inputField = document.getElementById("input");inputField.oninput = function () {console.log(inputField.value);};
Zadaci za interaktivni rad:
-
Napraviti dugme koje menja veličinu fonta u paragrafu sa id="demo" na 20px (i boju slova u zeleno).
-
Promeniti tekst u paragrafu sa id="demo" u "DOM je moćan!"
- Dodati novi element u postojeći koristeći
document.createElement()iappendChild().
Pitanje za razmišljanje: Šta sve možemo da uradimo sa JavaScript-om u DOM-u? KLIK da vidiš/sakriješ odgovor
- promeniti sve HTML elemente na stranici
- promenite sve HTML atribute na stranici
- promeniti sve CSS stilove na stranici
- ukloniti postojeće HTML elemente i atribute
- dodati nove HTML elemente i atribute
- reagovati na sve postojeće HTML događaje na stranici
- kreirati nove HTML događaje na stranici
U nastavku su materijali, postavljeni za rad kod kuće:
Prvo je potrebno na neki način "pronaći" te elementa na HTML stranici. Postoji više načina, a mi smo do sada pominjali samo neke od njih.
Moćemo da pronađemo HTML elemente na osnovu id-ja, naziva taga, naziva klase, CSS selektora ili colekcije unutar nekog objekta (ovo poslednje još nosmo pominjali).
Najlakše je pronaći element na osnovu id-ja:
Na primer, ako želimo da pronađemo element koji ima id="uvod":
const element =
document.getElementById("uvod");Ako postoji element koji ima taj id, metoda vraća element kao objekat (element).
Ako takav element ne postoji na stranici, unutar element će biti null.
A kako pronaći elemente na osnovu naziva tag-a ?
1. primer: kako pronaći sve <p> elemente: const element =
document.getElementsByTagName("p");
2. primer: prvo pronaći element koji ima id="main", a zatim sve <p> elemente unutar "main":
const x = document.getElementById("main");
const y = x.getElementsByTagName("p");
Kako pronaći sve elemente koji imaju isti naziv class ?
ovde se dobijaju svi elementi koji imaju class="intro":
const x =
document.getElementsByClassName("intro");
Kako pronaći sve elemente koji imaju isti neki od CSS selektora?
Selektora ima raznih (id, class name, type, attribute, value of attribute, ...).
U sledećem primeru se pronalaze svi <p> elementi koji imaju klasu class="intro":
const x =
document.querySelectorAll("p.intro"
Da se podsetimo:
- U DOM-u su svi HTML elementi definisani kao objekti.
- Način kako da im se pristupa i/ili programira (programski interfejs) su u stvari svojstva i metode svakog objekta.
- property: Svojstvo je vrednost koja može da se dobije ili postavi (kao što je promena sadržaja HTML elementa).
- method: Metoda je radnja koja može da se izvrši (kao što je dodavanje ili brisanje HTML elementa).
HTML DOM Document Object
Sa objektom document se predstavlja cela web stranica.
Ako treba da se pristupi nekom elementu na HTML stranici, uvek se počinje tako što se prvo pristupa objektu document.
(klik na obojeni deo teksta za PRIKAZ ili SAKRIVANJE)
Finding HTML Elements
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| document.getElementById(id) | Find an element by element id |
| document.getElementsByTagName(name) | Find elements by tag name |
| document.getElementsByClassName(name) | Find elements by class name |
Changing HTML Elements
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| element.innerHTML = new html content | Change the inner HTML of an element |
| element.attribute = new value | Change the attribute value of an HTML element |
| element.style.property = new style | Change the style of an HTML element |
| Method | Description |
| element.setAttribute(attribute, value) | Change the attribute value of an HTML element |
Adding and Deleting Elements
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| document.createElement(element) | Create an HTML element |
| document.removeChild(element) | Remove an HTML element |
| document.appendChild(element) | Add an HTML element |
| document.replaceChild(new, old) | Replace an HTML element |
| document.write(text) | Write into the HTML output stream |
Adding Events Handlers
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| document.getElementById(id).onclick = function(){code} | Adding event handler code to an onclick event |
Finding HTML Objects
The first HTML DOM Level 1 (1998), defined 11 HTML objects, object collections, and properties. These are still valid in HTML5.
Later, in HTML DOM Level 3, more objects, collections, and properties were added.
| Property | Description | DOM |
|---|---|---|
| document.anchors | Returns all <a> elements that have a name attribute | 1 |
| document.baseURI | Returns the absolute base URI of the document | 3 |
| document.body | Returns the <body> element | 1 |
| document.cookie | Returns the document's cookie | 1 |
| document.doctype | Returns the document's doctype | 3 |
| document.documentElement | Returns the <html> element | 3 |
| document.documentMode | Returns the mode used by the browser | 3 |
| document.documentURI | Returns the URI of the document | 3 |
| document.domain | Returns the domain name of the document server | 1 |
| document.embeds | Returns all <embed> elements | 3 |
| document.forms | Returns all <form> elements | 1 |
| document.head | Returns the <head> element | 3 |
| document.images | Returns all <img> elements | 1 |
| document.implementation | Returns the DOM implementation | 3 |
| document.inputEncoding | Returns the document's encoding (character set) | 3 |
| document.lastModified | Returns the date and time the document was updated | 3 |
| document.links | Returns all <area> and <a> elements that have a href attribute | 1 |
| document.readyState | Returns the (loading) status of the document | 3 |
| document.referrer | Returns the URI of the referrer (the linking document) | 1 |
| document.scripts | Returns all <script> elements | 3 |
| document.strictErrorChecking | Returns if error checking is enforced | 3 |
| document.title | Returns the <title> element | 1 |
| document.URL | Returns the complete URL of the document | 1 |